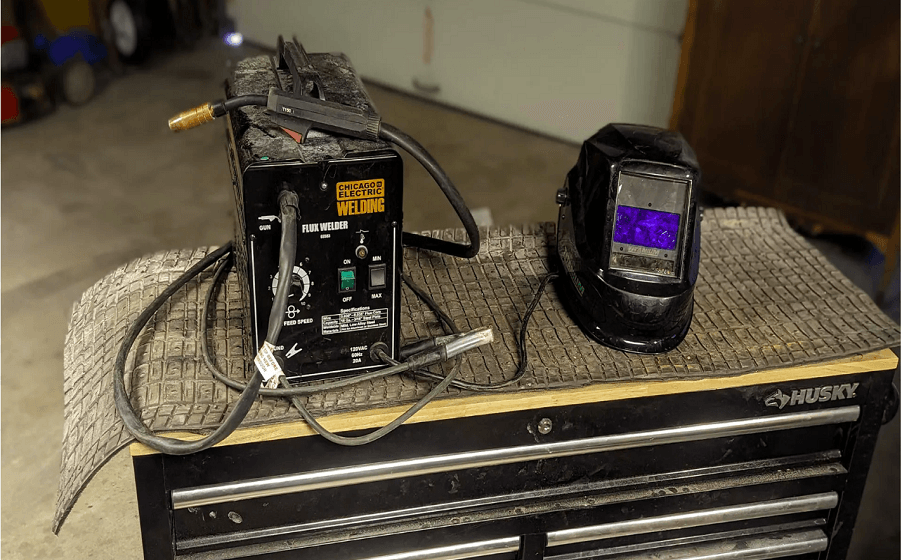
Chicago Electric MIG 170 Electric Feed Welder

Welder use and care
- Do not use the welder if the switch does not turn it on and off. Any welder that cannot be controlled with the switch is dangerous and must be repaired.
- Disconnect the plug from the power source before making any adjustments, changing accessories, or storing welders. Such preventive safety measures reduce the risk of starting the welder accidentally.
- Prevent unintentional starting. Ensure the switch is in the off-position before connecting to a power source or moving the welder. Carrying or energizing welders that have the switch on invites accidents.
Specifications
Setup
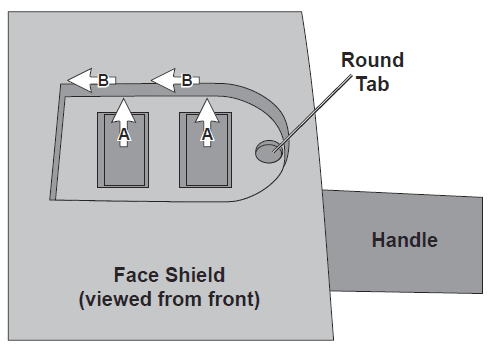
Face Shield Assembly
- Attach the handle to the Face Shield by lining up the two rectangular tabs on the handle with the corresponding holes in the face shield.
- A. press the tabs through the holes and then
- B. Slide the tabs forward from the back, locking the round tab in place.

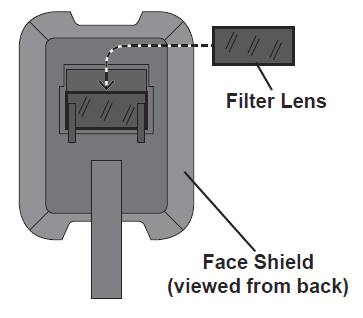
- Wear heavy-duty work gloves, the edges of the filter lens may be sharp. Remove any protective film from both sides of the filter lens. Slide the filter lens into the helmet behind the holding tabs. Make sure that the filter lens fits securely and that light cannot leak around its edges.

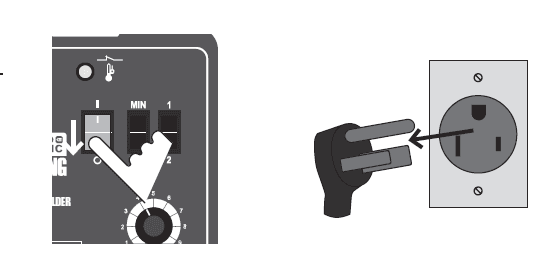
Plug Attachment
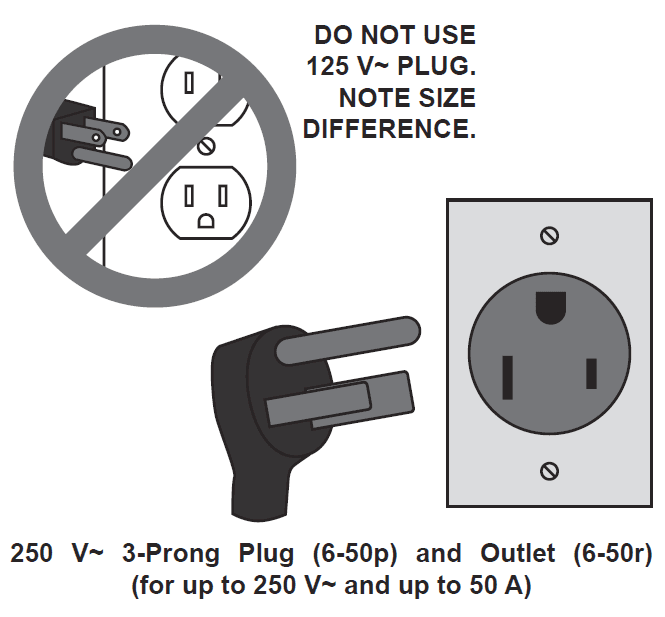
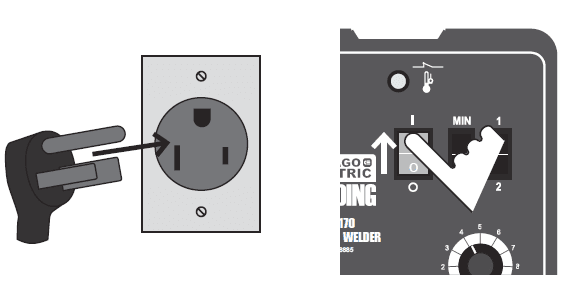
- A 250 V~ plug will need to be installed by a certified electrician before use.
- The plug shown is for use on a 50 A circuit. A different 250 V~ plug and outlet combination may be used, provided it is rated to handle the electrical requirements of the tool and is installed by a certified electrician.

- Note: Although 125 V~ plugs may look similar, the required plug is much larger, see illustration
Wire Spool Installation
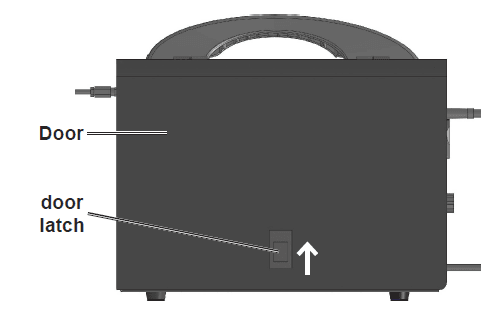
- Turn the welder OFF and unplug it before proceeding.

- Pull up on the door latch, then open the Door.

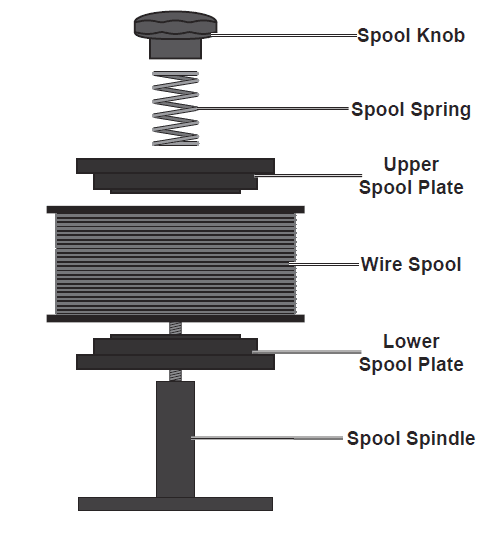
- Remove the Spool Knob, Spool Spring, and upper Spool Plate. If replacing a Spool, remove the old Spool and all remaining wire from the liners.
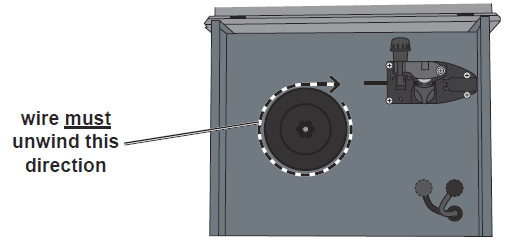
- Place the new Wire Spool over the Spool Spindle and on top of the lower Spool Plate as illustrated. To prevent wire feed problems, set the Spool so that it will unwind clockwise.

- Secure the Spool in place with the upper Spool Plate (narrower end against the Spool), then the Spool Spring and Spool Knob

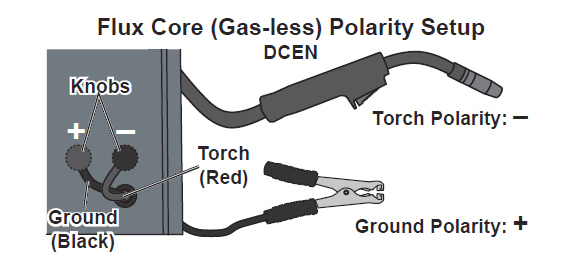
- 6a. Flux Core (Gas-less) Wire Setup: Remove the two Knobs securing the cables. Connect the Black Ground Cable to the rear, red, positive Terminal using the Knob. Connect the Red Torch Cable to the front, black, negative Terminal using the other Knob. This is the initial setup, called Direct Current Electrode Negative (DCEN)

- 6b. Solid Core (Gas Shielded) Wire Setup:

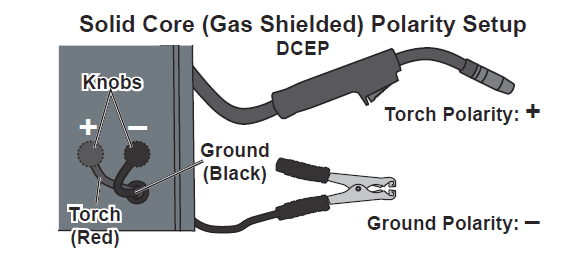
- a. Remove the two Knobs securing the cables. Connect the Black Ground Cable to the front, black, negative Terminal using the Knob. Connect the Red Torch Cable to the rear, red, positive Terminal using the other Knob. This is called Direct Current Electrode Positive (DCEP).
- b. Determine which type of shielding gas would be appropriate for the welding you will do – see chart on welder
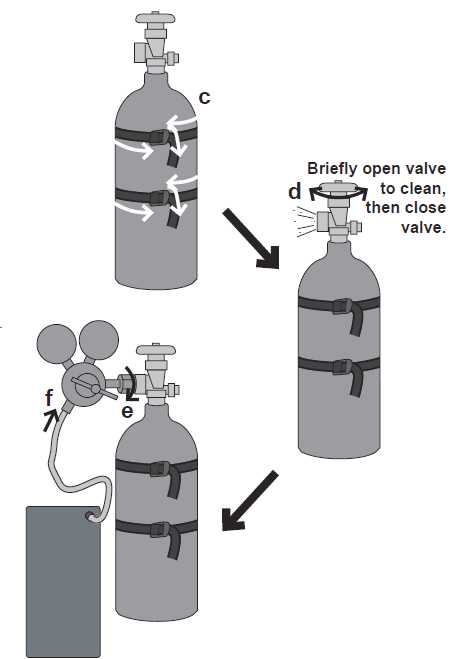
- c. With assistance, set the cylinder (not included) onto a shelf or cart near the welder and secure the cylinder in place with two straps (not included).
- d. Remove the protective cap from the cylinder (if present). Stand to the side of the valve opening, and open the valve briefly to blow dust and dirt from the valve opening. Close the cylinder valve.

- 6b. Solid Core (Gas Shielded) Wire Setup:
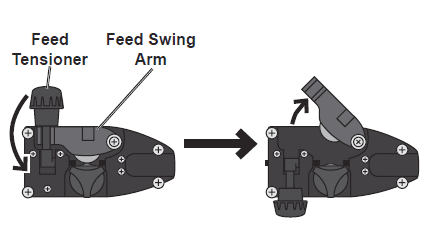
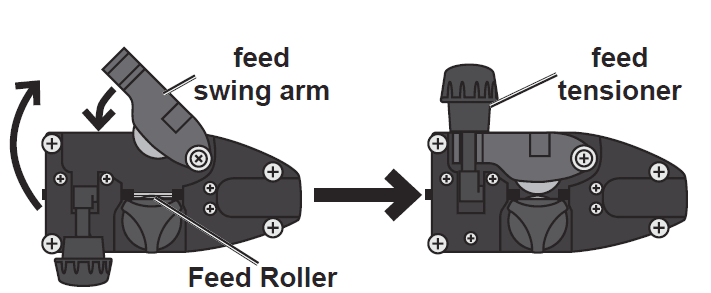
- Turn the Feed Tensioner knob counterclockwise to loosen it enough to pull it down to remove tension. (Do not loosen the Tensioner knob too much, or the Tensioner will come apart.) Then, swing the Feed Swing Arm up.

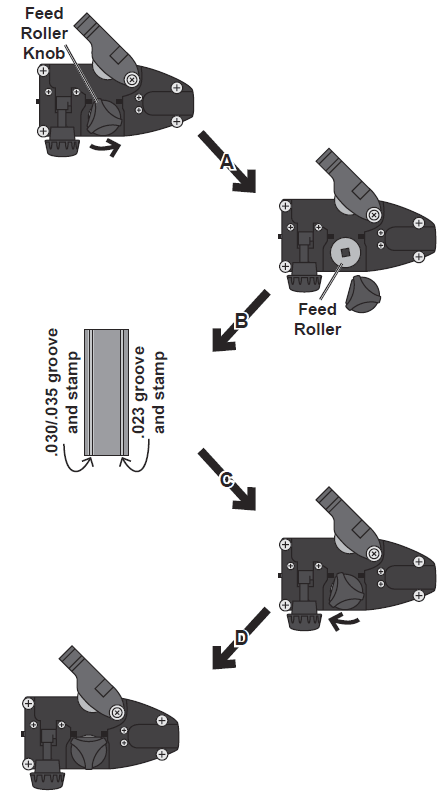
- Feed Roller Instructions:
Check that the Feed Roller is turned to properly match the wire size marked on the Wire Spool:- A. Twist the Feed Roller Knob about 1/3 of a turn counterclockwise until it stops.
- B. Pull the Feed Roller Knob straight off to expose the Feed Roller.
- C. Flip the Feed Roller as needed and confirm that the number facing you is the same as the wire diameter on the Spool. (0.8mm = .030″ & 0.6mm = .023″)
- D. Place the Feed Roller Knob back into place in the same orientation it was removed in, and twist it about 1/3 of a turn clockwise to secure it.

- IMPORTANT:
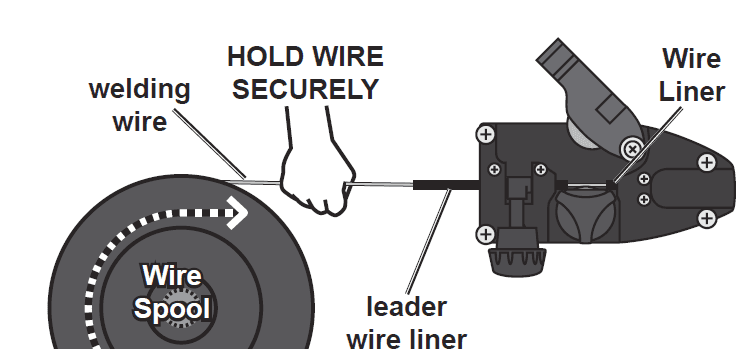
- Securely hold onto the end of the welding wire and keep tension on it during the following steps. If this is not done, the welding wire will unravel and create a tangled “bird’s nest”, wasting wire.
- Cut off all bent and crimped wire. The cut end must have no burrs or sharp edges; cut again if needed.
- Keep tension on the wire and guide at least 12 inches of wire into the Wire Liners.

- Swing the wire feed swing arm down, and swing the feed tensioner up to latch it across the tip of the arm. Make sure the Welding Wire is resting in the bottom groove of the Feed Roller, then turn the feed tensioner knob clockwise a couple of turns. After the wire is held by the tensioner, you may release it.

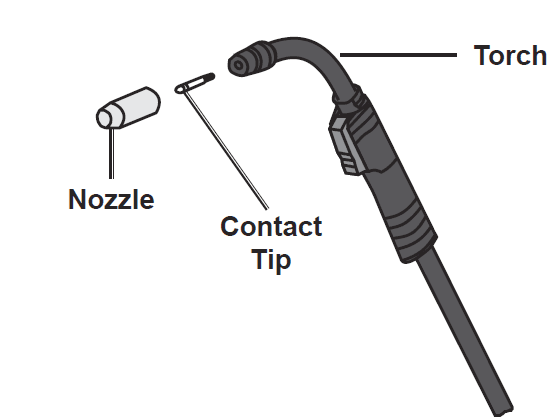
- Pull the Nozzle to remove it.

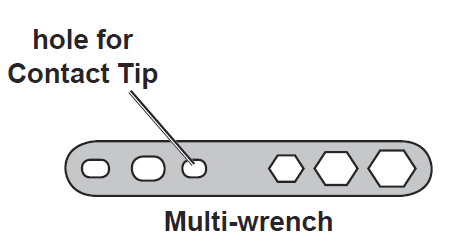
- Using the third oval hole on the Multi‑wrench, turn the Contact Tip counterclockwise and remove.

- Lay the Torch Cable out in a straight line so that the wire moves through it easily. Leave the cover open, so that the feed mechanism can be observed.
- Do not touch the Torch’s Trigger. Plug the Power Cord into its electrical outlet and turn the welder ON.

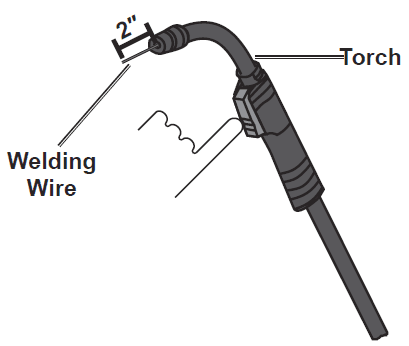
- Point the Torch away from all objects and press the trigger until the wire feeds through two inches. The wire liner may come out with the welding wire, this is normal, just push the wire liner back into the Torch. If the wire does not feed properly and the Spool is stationary, turn the welder OFF, unplug it, and slightly
tighten the feed tensioner clockwise before retrying.
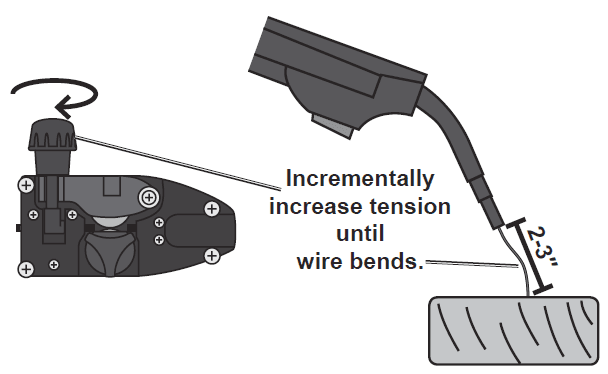
- To check the wire’s drive tension, feed the wire against a piece of wood from 2 to 3 inches away. If the wire stops instead of bending, turn the welder OFF, unplug it, slightly tighten the feed tensioner clockwise, and try again. If the wire bends from the feed pressure, then the tension is set properly.

- TURN THE WELDER OFF.

Control Panel Layout
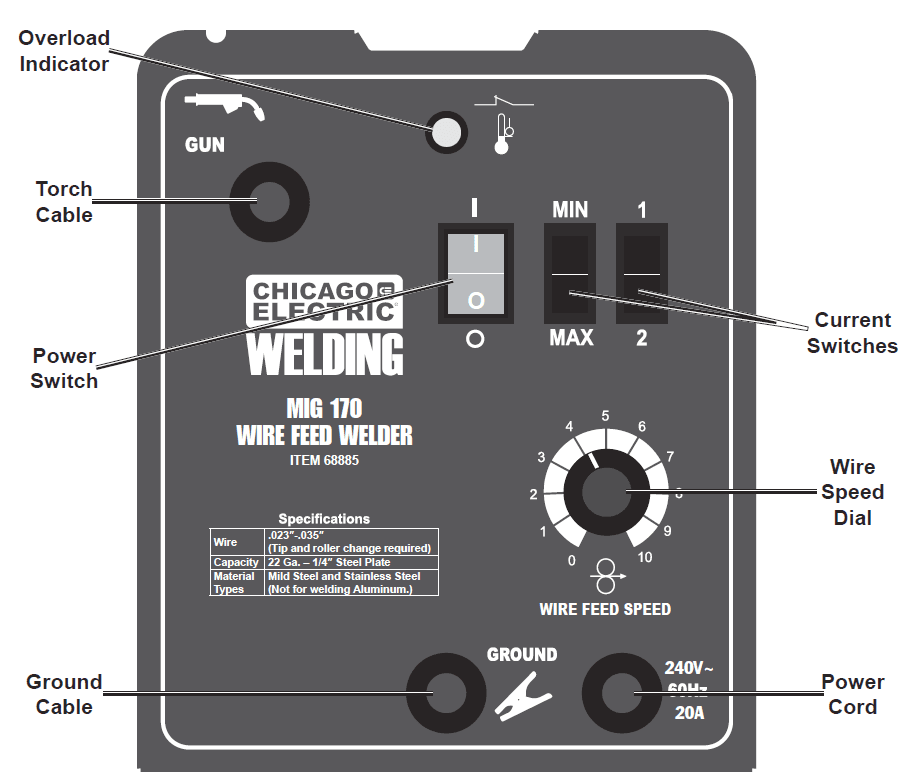
- Overload Indicator:
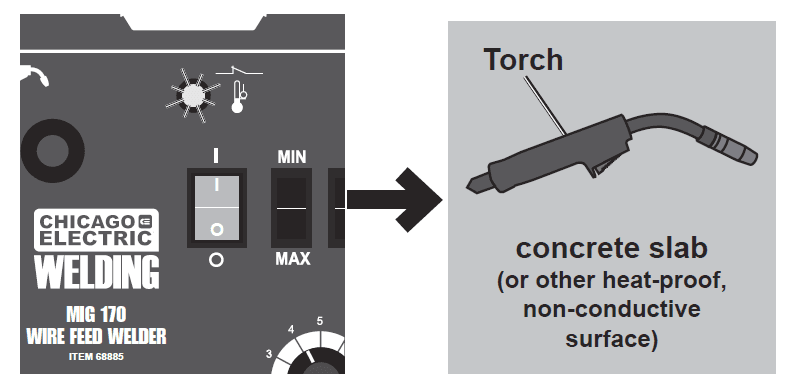
- This lights up if the duty cycle work period is exceeded, resulting in overheating the welder. Rest the Torch on an electrically non‑conductive, heat-resistant surface, such as a concrete slab, well clear of the ground clamp while allowing the welder to cool with the Power Switch on, so the Fan can help cool the welder. Once the welder cools enough to be used again, use shorter welding periods and longer rest periods to prevent needless wear.
- Power Switch:
- This turns on power to the welding Torch and internal cooling fan. The welding Torch is energized whenever the Power Switch is on.
- Current Switches:
- These control the output amperage of the welder. Adjust them according to the weld settings chart to achieve a good weld.
- Wire Speed Dial:
- This controls the speed that the welding wire feeds out of the welding Torch and adapts output amperage somewhat. Adjust this according to the weld settings chart to achieve a good weld.
- Power Cord:
- Plug the Power Cord into a properly grounded 240 V~ (at least 30 amp rating) outlet with a delayed action type circuit breaker or fuses.
- Torch Cable:
- The welding Torch connects here. The wire and welding current feeds to the weld through here.
- Ground Cable:
- This connects to the base metal to provide a good connection for the current to travel back to the welder.
Duty Cycle (Duration of Use)
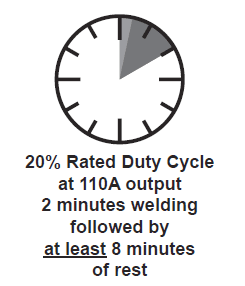
- Avoid damage to the Welder by not welding for more than the prescribed duty cycle time. The Duty Cycle defines the number of minutes, within a 10-minute period, during which a given welder can produce a particular welding current without overheating. For example, this Welder with a 20% duty cycle at rated output (110A) must be allowed to rest for at least 8 minutes after every 2 minutes of continuous welding.

- Failure to carefully observe any duty cycle limitations can easily over-stress a welder’s power generation system contributing to premature welder failure.
- This welder has an internal thermal protection system to help prevent this sort of over-stress. When the unit overheats, it automatically shuts down, and the Overload Indicator lights, then the welder automatically returns to service after cooling off. Rest the Torch on an electrically non-conductive, heat‑proof surface, such as a concrete slab, well clear of the ground clamp while allowing the welder to cool with the Power Switch on, so that the internal Fan will help cool the welder. When the welder can be used again, use shorter welding periods and longer rest periods to prevent needless wear.

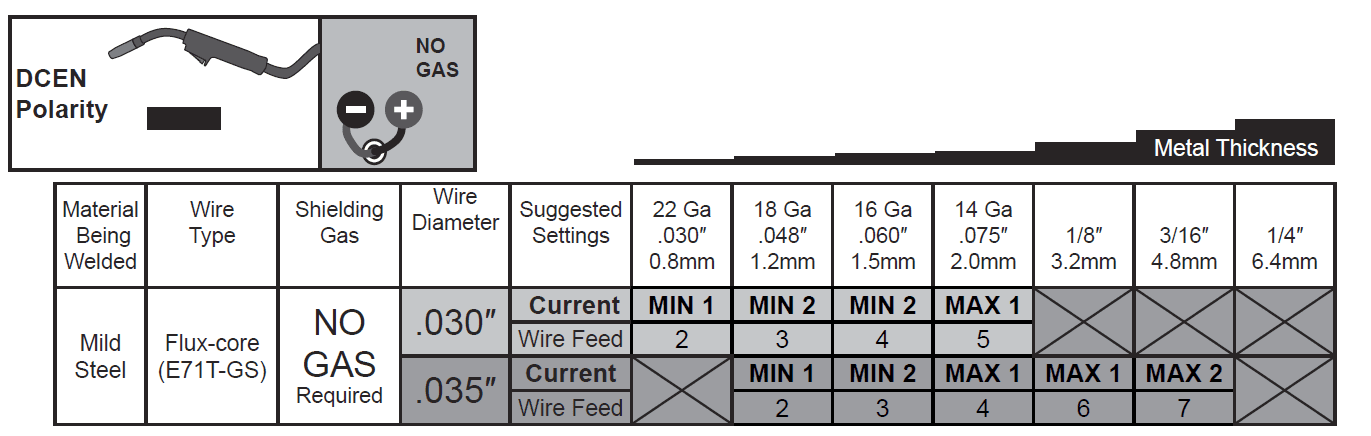
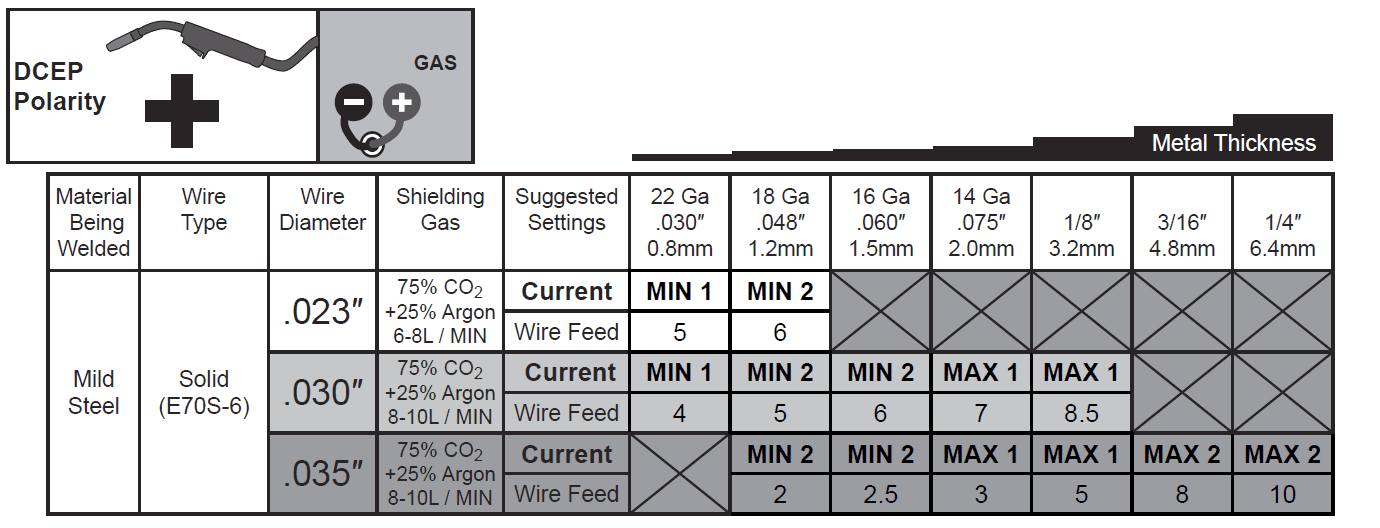
- Note: The following charts are only intended to show general guidelines for different wire sizes and for different thicknesses of material. The settings should only be used at the beginning of a weld and must be adjusted after stopping and carefully inspecting the weld. Proper welding takes experience.
Flux Weld Settings
MIG Weld Settings
For more manuals by Chicago Electric, visit ManualsLibraryy
Chicago Electric MIG 170 Electric Feed Welder-FAQs
What voltage and wire speed are recommended for MIG welding?
The voltage and wire speed depend on the wire size. For a 0.024-inch wire, use 13–15 volts and 130–160 inches per minute (ipm) feed speed. For a 0.030-inch wire, use 15–17 volts and 75–100 ipm.
How many amps does the Chicago Electric MIG 170 welder use?
The Chicago Electric 125 Flux Welder operates at 125 amps and is capable of welding materials from 18-gauge to 3/16-inch thick steel using 120-volt power.
How does a MIG welder work?
A MIG welder uses a constant voltage power supply to create an electric arc that fuses a base metal with a continuously fed filler wire. Simultaneously, an inert shielding gas protects the weld pool from contamination.
How do I calculate the amps needed for MIG welding?
A general rule is 1 amp per 0.001-inch material thickness. For example, a 0.125-inch material requires 125 amps.
How much power does an electric welder use?
Power consumption depends on the machine type and material. Spot welders use 5,000–15,000 watts, while seam welders may use 10,000–50,000 watts.
What gas is used for MIG welding?
Argon is the primary gas for MIG welding. Helium can be added to improve penetration and weld pool fluidity. Argon or argon/helium mixtures work for all material grades.
How do I calculate welder wattage?
Multiply the voltage by the welder’s amperage. For example, a 120V welder drawing 15 amps uses 1,800 watts, while a 240V welder drawing 30 amps uses 7,200 watts.
What size breaker do I need for a MIG welder?
A 208–230V welder requires at least a 30A breaker, with 50A recommended for welding at up to 180 amps. For outputs of 200 amps or more, a 50A breaker is necessary.